

Help appropriate patients simplify dosing by choosing the only Sertraline HCl Capsules in 150 mg or 200 mg dosages.*1
For Major Depressive Disorder and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder1
Do not initiate treatment with Sertraline HCl Capsules. Use another Sertraline HCl product for initial dose titration and dosages below 150 mg once daily.1
A real-world retrospective analysis showed that patients taking one pill a day (vs multiple pills) improved adherence.2
Stabilized patients on a lower pill burden had statistically higher adherence and were more likely to remain persistent throughout the 1-year post-index period vs patients on a higher pill burden but the same overall dose.2
Probability of remaining persistent on sertraline†
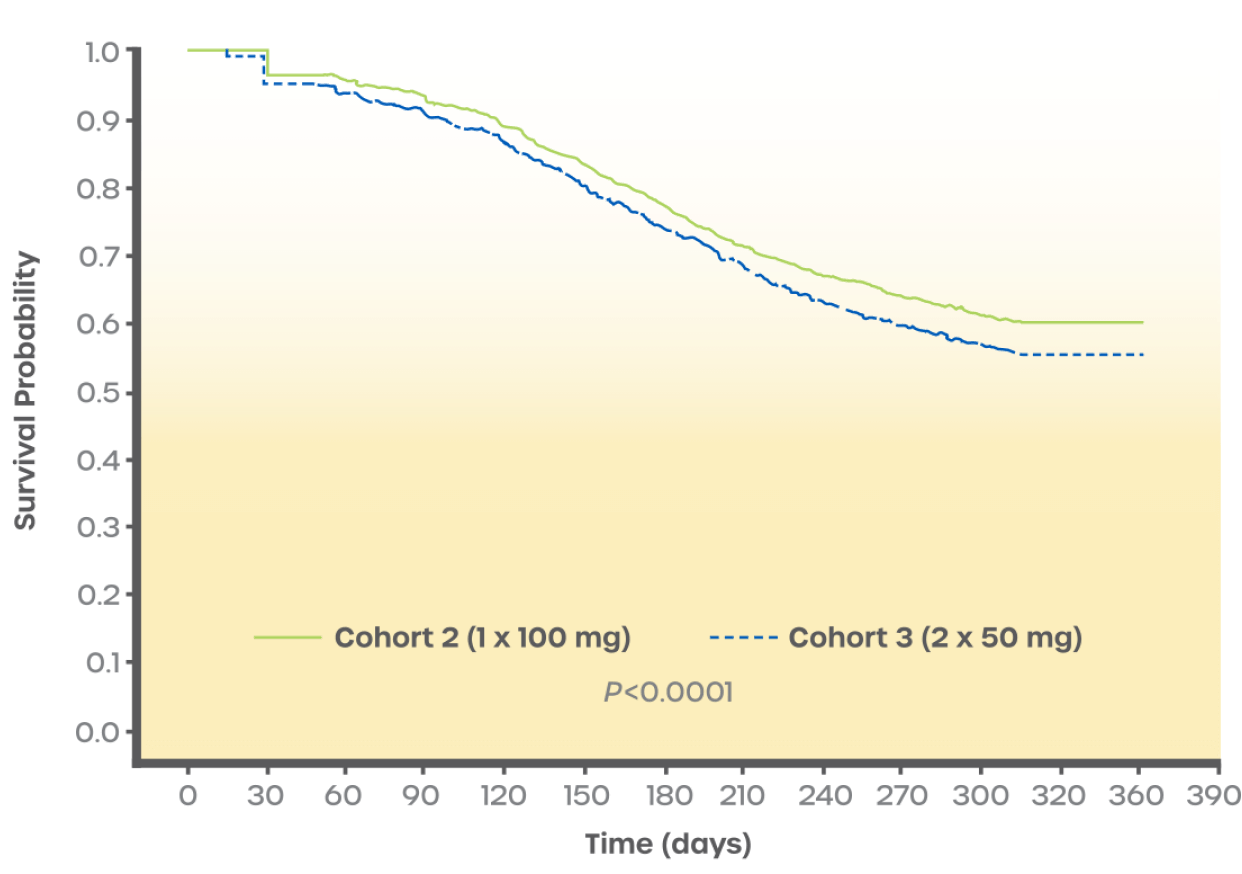
Kaplan-Meier survival curves for probability of remaining persistent with sertraline during the 1-year post-index period for patients who achieved stable dose on different pill regimens. This chart shows Cohort 2 (1 x 100 mg) vs Cohort 3 (2 x 50 mg).2
To view the complete retrospective study, including this graph and a table of the number of people in each cohort, see Wang G, et al. Int J Clin Pract. 2021.
NOTE: The sertraline tablets referred to in this study were not Almatica products.
Eligible, commercially insured patients could pay as little as $10 per month, automatically applied at the pharmacy, no copay card necessary.
Automatic savings at the pharmacy counter with an eVoucher
Eligible, commercially insured patients enjoy automatic savings at over 50,000 pharmacies nationwide. Copay savings are automatically applied at the pharmacy counter, without any action required by the patients.
Important Safety Information
INDICATION FOR USE
Sertraline HCl Capsules is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder in adults and obsessive-compulsive disorder in adults and pediatric patients 6 years and older.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sertraline HCl Capsules is contraindicated in patients:
- Taking, or within 14 days of stopping, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome
- Taking pimozide
- With known hypersensitivity to sertraline or the excipients in Sertraline HCl Capsules (eg, anaphylaxis, angioedema)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Serotonin Syndrome
- Sertraline HCl Capsules can precipitate serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. The risk is increased with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin.
Increased Risk of Bleeding
- Sertraline HCl Capsules increases the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), other antiplatelet drugs, warfarin, and other anticoagulants may add to this risk. There is an association between drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding. Exposure to SSRIs, particularly in the month before delivery, has been associated with a less than 2-fold increase in the risk of postpartum hemorrhage.
Activation of Mania or Hypomania
- In patients with bipolar disorder, treating a depressive episode with Sertraline HCl Capsules may precipitate a mixed/manic episode. Prior to treatment, screen patients for any personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania.
Discontinuation Syndrome
- Adverse reactions after discontinuation of serotonergic antidepressants, particularly after abrupt discontinuation, include: nausea, sweating, dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances, tremor, anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, hypomania, tinnitus, and seizures. A gradual reduction in dosage rather than abrupt cessation is recommended.
Seizures
- Sertraline HCl Capsules has not been systematically evaluated in patients with seizure disorder and should be prescribed with caution in these patients.
Angle-Closure Glaucoma
- Sertraline HCl Capsules may trigger an angle closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy. Avoid use in patients with untreated anatomically narrow angles.
Hyponatremia
- Hyponatremia may occur with Sertraline HCl Capsules. In patients with symptomatic hyponatremia, discontinue Sertraline HCl Capsules and institute appropriate medical intervention. Elderly patients, patients taking diuretics, and those who are volume-depleted may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia.
False-Positive Effects on Screening Tests for Benzodiazepines
- False-positive urine immunoassay screening tests for benzodiazepines have been reported in patients taking another Sertraline HCl product and may be expected for several days following discontinuation of sertraline.
QTc Prolongation
- During post-marketing use of sertraline, cases of QTc prolongation and Torsade de Pointes (TdP) have been reported. Sertraline should be used with caution in patients with risk factors for QTc prolongation.
Reactions to FD&C Yellow No. 5 (Tartrazine)
- Sertraline HCl Capsules contain FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine), which may cause allergic-type reactions in certain individuals, seen frequently in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity.
Sexual Dysfunction
- Sertraline HCl Capsules may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction. In male patients, use may result in ejaculatory delay or failure, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction. In female patients, use may result in decreased libido and delayed or absent orgasm.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most frequent adverse reactions in pooled placebo-controlled clinical trials were nausea, diarrhea / loose stool, tremor, dyspepsia, decreased appetite, hyperhidrosis, ejaculation failure, and decreased libido. In trials for major depressive disorder, somnolence was also seen. In trials for obsessive-compulsive disorder, insomnia and agitation were also seen.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Monitor for adverse reactions, and reduce dosage of Sertraline HCl Capsules or other protein-bound drugs (eg, warfarin) as warranted.
- Decrease the dosage of drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 if needed. Conversely, an increase in dosage of a CYP2D6 substrate may be needed if Sertraline HCl Capsules are discontinued.
- Sertraline HCl Capsules may increase phenytoin concentrations. Monitor phenytoin levels, and reduce dosage if needed.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Use of Sertraline HCl Capsules in the month before delivery may be associated with an increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage. Third trimester use may increase risk for neonatal complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding—and/or persistent pulmonary hypertension and withdrawal in the neonate.
Hepatic Impairment
Sertraline HCl Capsules are not recommended in patients with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment.
For additional safety information about Sertraline HCl Capsules, see the Full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING, and Medication Guide.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to Almatica at 1-877-447-7979 or the FDA at www.fda.gov/medwatch, or call 1-800-FDA-1088.


